Abstract
Purpose Targeted drug delivery vehicles with low immunogenicity and toxicity are needed for multiple myeloma (MM) therapy. Exosomes are appropriate drug delivery vehicles for targeted drug delivery because of their small size, stable structure, non-immunogenicity, and non-toxic nature. We developed activated monocytes exosome-based targeted delivery platform for Bortezomib.
Methods and Results
Isolation and characterization of anti-BCMA-EXO
Activated monocytes-derived exosomes were purified by ultracentrifugation and determined by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and transmission electron microscope (TEM).
The myeloma targeting capability of exosomes was conferred by engineering the monocytes to express anti-BCMA. B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is an excellent target for immunotherapy in MM. To confer targeting capabilities, plasmids encoding the anti-BCMA constructs were transfected into the monocytes before exosomes purification. The sequence of anti-BCMA was obtained from the patent (CN201780031233.X). Anti-BCMA was strongly expressed in monocytes, was incorporated into the monocyte-derived exosomes and was localized to the external exosomal surface by flow cytometry. This modification did not appear to affect the physical properties of the modified exosomes based on NTA and TEM.
In vitro targeting of anti-BCMA-EXO
To investigate whether anti-BCMA-EXO are able to bind to BCMA-positive myeloma cells, anti-BCMA-EXO or blank-Exos were labeled with PKH67 and cultured with the myeloma cell lines LP-1 and U266, which have been detected to highly express BCMA on its surface. Flow cytometry demonstrated that anti-BCMA-Exos bound to myeloma cells more efficiently than blank-Exos.
In vitro antimyeloma effect of anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz
We loaded Bortezomib into anti-BCMA-modified exosomes by electroporation. The exosomes loaded with Bortezomib were quantified for the encapsulated Bortezomib by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC).
We then analyzed the ability of anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz to inhibit myeloma cell proliferation. Myeloma cell lines U266 and LP-1 were treated with control medium, blank-EXO, blank-EXO-Btz, anti-BCMA-EXO, anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz and an equivalent dose of free Btz. A significant suppression of cell proliferation was observed in the anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz treated cells. And blank-EXO had a slight inhibition effect on cells. LC-MS/MS was performed to detect exosome-associated protein. Proteins of EXO were enriched in the apoptotic pathway.
In vivo antimyeloma efficacy of anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz
To evaluate the efficacy of anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz in vivo, orthotopic MM xenograft models were established. Luciferase labelled myeloma cell line LP-1 cells were injected via the lateral tail vein in NSG mice.
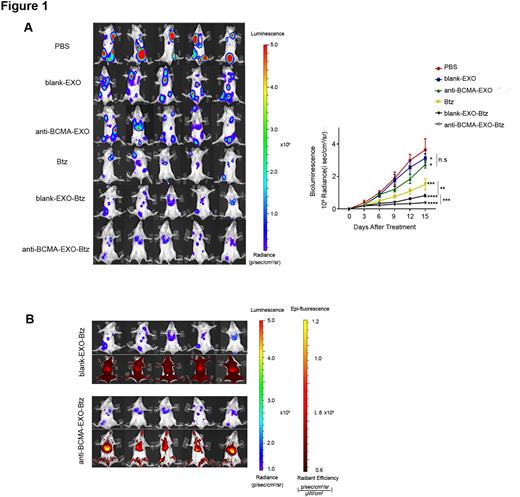
We first assessed the capacity of the anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz to inhibit myeloma. Mice were sorted into six groups: PBS, blank-EXO, blank-EXO-Btz, anti-BCMA-EXO, anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz and an equivalent dose of free Btz. A significant suppression of tumor growth was observed in the mice treated with anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz, indicating the specific myeloma targeting ability of anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz.
To investigate the potential of anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz to specifically deliver Btz to the myeloma in vivo, exosomes were labelled using VivoTrack Dil (Fluorescence). The labelled EXO were injected into mice via the tail vein injection. The locations of injected exosomes were monitored in real time over 8 h using in vivo optical imaging system. The fluorescence signal from anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz was detected at the myeloma sites, while blank-EXO-Btz distributed all over the body. To further analyze the fate of the injected EXO. we removed the organs of interest 2 h after injection. Ex vivo fluorescence imaging showed more stronger fluorescence signals in the liver and spleen from mice treated with blank-EXO-Btz than those from mice treated with anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz. These data suggested that anti-BCMA-EXO-Btz specifically targeting Btz to the myeloma in vivo.
Conclusion Here we show that exosomes, endogenous nano-sized membrane vesicles secreted by monocytes, can deliver Btz to myelomas. Our results suggest that exosomes modified by targeting ligands can be used therapeutically for the delivery of Btz to myelomas, thus having great potential value for clinical applications.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal